LLM explained
LLM – When AIs find their voice
“Explain to me what an LLM is.” If you ask this question to ChatGPT, it will answer instantly—and for good reason: it is one!
These Large Language Models (LLMs) have become indispensable and hide behind many of the tools we use every day, often without our realizing it: search engines, voice assistants, automatic translators, chatbots…
At Neovision, we master these technologies and integrate them into our solutions. Drawing on this expertise, we invite you to explore how they work, their uses, and their evolution to better understand how they are transforming our daily lives.
“Tell me: what is an LLM?”
The Mystery Unveiled
These LLMs are artificial-intelligence models specialized in the processing and generation of text, images, and sound. They produce an output based on an input provided by the user, called a ‘prompt‘, a query that guides the model in its response.
Example of how an LLM works using ChatGPT
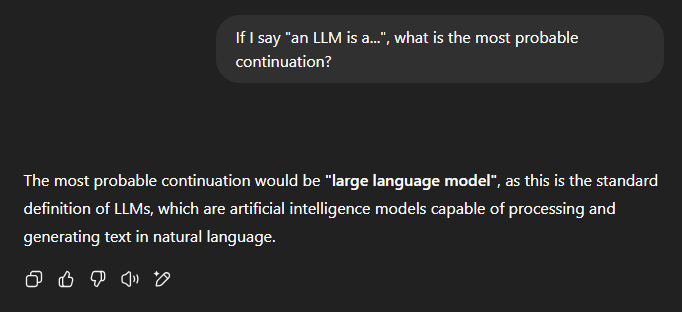
Contrary to popular belief, they do not understand language as a human would. When asked a question, they generate a response iteratively, predicting the most probable next word one at a time. Each new word is influenced by those already generated, giving the illusion of structured reasoning when, in reality, it is a probabilistic chain built on knowledge acquired from millions of texts during training.
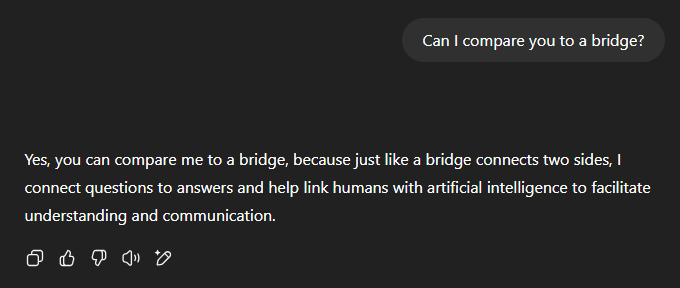
LLMs belong to the field of NLP (Natural Language Processing), which enables machines to understand human language. An LLM is a bridge—an intermediary—between AI and humans. Whereas interacting with conventional AI required code or commands, an LLM makes AI accessible to everyone: no technical skills needed, just write to it or speak.
From inaccessible to indispensable: the ascent of LLMs
Starting the Engine
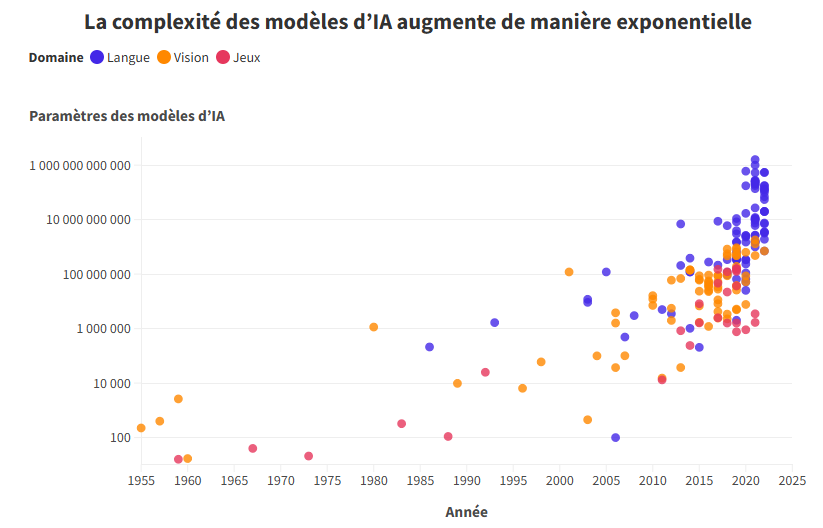
In 1950, Alan Turing published Computing Machinery and Intelligence and introduced the Turing Test, which gauges whether a machine can fool a human about its nature during a conversation: Can a machine think? Today, some LLMs have passed this test, proving how far Artificial Intelligence has come and how convincing these models have become.
What enabled LLMs to emerge and gain popularity:
1 – Computing power
Advances in processors—especially GPUs (graphics cards originally created for video games)—allow enormous volumes of data to be processed at high speed.
In 2018, training GPT-2 (1.5 billion parameters) took several months, but in 2023 ChatGPT-4 (170 billion) was trained in just a few weeks.
2 – Data explosion
Thanks to the Internet, AIs have gained access to a massive amount of text for training. An LLM processes text via “tokens”, units that may be a word, part of a word, or a character.
In 1992, only a handful of websites existed worldwide; today there are more than two billion—plenty to feed our LLMs!

3 – Technological breakthroughs
Deep Learning and Transformers : These advances enable models to understand not only the meaning of words and texts, but also their context, capturing irony, double meanings and expressions.
An LLM can distinguish the meaning of the word bass according to its usage: a bass guitar (instrument) or a low altitude (pitch).
Since 2018, LLMs have undergone a spectacular evolution and widespread adoption, especially with the arrival of GPT-3 and GPT-4. These advances have made LLMs accessible to everyone.
The most famous LLMs mainly come from the United States, with models such as GPT-4o from OpenAI used in ChatGPT, but there are also European models like Mistral, developed in France.
GPT-4 – OpenAI

Gemini – Google DeepMind

Claude – Anthropic

LLaMA – Meta

Mistral – Mistral AI

From magic to mastery, the power is in your hands
Controlled Logic
Using an LLM depends on the objective you are pursuing and the resources available.

Existing LLM or custom-built?
Using an existing LLM is the simplest and fastest solution. For example, with ChatGPT, any user can ask questions without technical skills. In addition, APIs integrate LLM capabilities into existing tools (chatbots, CRMs, etc.), automating tasks without the need to develop a full model.
Creating a custom LLM is possible, but it requires enormous resources (GPUs, energy, time…) and can quickly become obsolete. For instance, adapting a model such as LLaMA 2 to a specific domain by training it on new data (fine-tuning) does specialize it, but when a new version appears (LLaMA 3), the process has to start again.

Open Source or Closed Source?
An Open-Source model, such as LLaMA, is freely accessible and can be used, improved, and adapted by anyone, allowing companies and developers to create custom applications built on an existing model.
Conversely, a Closed-Source (proprietary) model, such as ChatGPT, is controlled by a company: it can be used through an interface or API, but its code cannot be viewed or modified.

Best practices to adopt
Even though accessing an LLM is easy, using it effectively requires a few best practices.
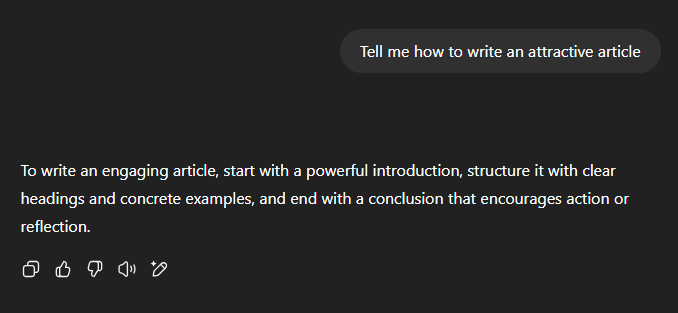
It is essential to give as much context as possible in your prompt to get more precise answers. Put yourself in the model’s shoes: an LLM cannot guess the meaning or intention behind a vague request; if the answer does not suit you, the prompt often needs improvement. Do not hesitate to detail your request (tone, objective, situation, audience…), adjust it based on the results obtained, and verify the information, especially in specialized fields.
The solution to reinvent your operations
Unleash the Magic
LLMs are transforming both our professional and personal lives, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and creativity. They automate tasks, freeing up time for higher-value missions while offering personalized solutions. Every sector benefits.
Creation and writing
Automated writing: e-mails, reports, documentation…
Smart summarization: text summaries and analyses
Multimedia creation: text, visuals, videos…
Data analysis and processing
Smart organization: sorting, classifying, and analyzing data
Strategic studies: in-depth market analysis
Advanced exploration: large-scale information extraction
Translation and linguistic adaptation
Automatic translation: smooth conversion into different languages
Tailored adaptation: adjusting content to culture and tone
Software development and code creation
Intelligent assistance: help with writing and debugging code
Optimization and automation: improvement suggestions and time savings
Customer service and support
Automated assistance: FAQs, chatbots, and instant replies
Optimized experience: anticipating customer needs
Proactive follow-up: request management and interaction tracking
Personal assistance
Instant answers and smart web search
Organization: time, reminders, and task planning
Suggestions: personalized recommendations
LLMs can be integrated into tools to boost their performance and meet specific needs.
For example, with RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), an LLM searches external databases not contained within the model before formulating its response, enabling it to go beyond its training knowledge and provide more precise, up-to-date, and context-appropriate answers.
Another example is AI Agents: intelligent assistants driven by LLMs, capable of using tools to autonomously carry out tasks such as answering e-mails, scheduling meetings, or sorting and analyzing data.
Powerful tools, but challenges to face
Limits and Threats
LLMs are powerful tools, yet they come with limits and issues that must be anticipated to maximize their benefits while reducing associated risks.
“Hallucinations”: producing incorrect or invented answers that seem credible but are not based on any reliable source.
Ethics: Presence of bias (social, cultural, political…) in the training data that appears in generated answers.
Education: Dependence and misuse by students, which can harm learning and critical thinking.
Environment: Huge computing, energy, and water resources required to train and use models. According to the International Energy Agency, one ChatGPT query consumes ten times more energy than a Google search.
Security and privacy: Handling sensitive data, with risks of leaks, misuse, or regulatory non-compliance.
Sovereignty: LLM dominance by U.S. companies, raising issues of technological dependence and data control.
Malicious uses: Hijacking LLMs to generate misinformation, phishing, or automated propaganda. Here is one example.


To tackle these challenges, it is essential to train models on representative, diverse, and abundant data.
A regulatory framework is indispensable to control LLM use and ensure transparency and safety, as the AI Act does.
It is not always relevant to use LLMs; their use should not become systematic, especially because of their energy consumption. And let us not forget the importance of human reasoning!
Finally, it is crucial to favor responsible and ethical uses of AI, ensuring these technologies truly benefit businesses and society. At Neovision, we select projects that align with our values. AI and LLMs are neither good nor bad in themselves—it all depends on what we do with them.
The future of LLMs—and LLMs driving the future
Language Transforms
Language models are evolving at lightning speed and are becoming a driver of innovation across every sector. They are paving the way for advances that will further transform our daily lives and businesses.
Several trends are emerging: more specialized, less energy-hungry models like SLMs (Small Language Models); the evolution of multimodal models such as VLMs (Vision-Language Models that can analyze text and images simultaneously); the rapid development of AI Agents; the rise of Embedded AI in devices such as robots; and ever deeper integration of AI into our business processes.
But how far can this go? The question is no longer only how LLMs will evolve, but how to use them intelligently.
What if we imagined the next chapter together? As AI and LLM integration experts, we help our clients fully leverage these advances by designing custom solutions tailored to tomorrow’s challenges.
LLMs, although they have existed for several years, have experienced spectacular evolution and popularization. What once seemed reserved for researchers or experts is now within everyone’s reach.
Beyond the technical breakthrough, LLMs mark a genuine turning point in how we interact with AI. Their ability to understand and generate language opens new perspectives but also raises important questions about their use, limits, and impact.
As these technologies evolve, we must deploy them responsibly, balancing innovation with caution, so that they advance progress without compromising our values.